Does Veal Have More Iron Than Beef

vs

Summary
Beef is college in calories, protein, and fats; however, veal has a more favorable protein and fat quality. Beef is lower in cholesterol.
Veal is richer in virtually B group vitamins except for vitamin B12, which can be found in larger amounts in beef. Beef is also higher in iron and zinc.
The adverse effects of cherry meat are attributed to the high levels of saturated fats, cholesterol, and heme iron. Veal, being lower in all of these, tin can exist assumed to be the healthier choice.
Table of contents
- Introduction
- Nomenclature
- Advent
- Sense of taste and Use
- Price
- Varieties
- Diet
- Macronutrients and Calories
- Calories
- Fats and Cholesterol
- Protein and Carbohydrates
- Vitamins
- Minerals
- Glycemic Index
- Acidity
- Weight Loss & Diets
- Health Bear upon
- Wellness Benefits
- Cardiovascular Wellness
- Diabetes
- Downsides and Risks
- Cardiovascular Health
- Diabetes
- Cancer
- References
Introduction
Humans have been consuming the meat of cattle from prehistoric times. Cattle were domesticated in around 8500 BC, mainly due to the multitude of valuable products they could provide humans.
Today, bovine meat is among the virtually consumed meats in the world. This article will look at the two master types of bovine meats - veal and beefiness - comparison their nutritional values and health impacts to run into which meat is the better pick.
Nomenclature
Veal is the meat of calves: young domestic cows or bulls. Beef, on the other manus, is produced from older cattle.
Both veal and beef can exist produced from either sex activity of the cattle. Even so, veal is commonly cutting from the meat of young males of dairy cows, while most beef comes from young heifers and steers. Heifers are immature females, and steers are immature castrated males.
Beefiness and veal are classified as crimson meats due to the high levels of myoglobin and, therefore, the fe bound with it.
Appearance
While veal and beef are both red meats, beef is significantly darker in colour. Because of its high myoglobin content, beef is also higher in iron.
Taste and Utilize
Veal, notably, has a more tender texture and a more delicate sense of taste. Veal is also easier to digest when compared to beef.
Cattle meat is very versatile and is used in staple dishes from numerous cultures. Veal and beef can be cooked by grilling, barbecuing, broiling, roasting, frying, and many other ways.
Toll
According to the general market place value of meats, beefiness is slightly cheaper.
Varieties
Based on the cutting of the meat, both veal and beef can be called the chuck (shoulder), the brisket and shank (breast), the rib, the sirloin (hip), the curt loin, the short plate, the flake, and the round. These unlike cuts have varying culinary characteristics and are used according to those qualities.
Based on the weather condition in which the cows have been kept, veal can be formula-fed, also known every bit milk-fed or white, non-formula fed, likewise known every bit scarlet, pasture-raised, or free-raised, and bob veal. Bob veal is the meat of the calf, slaughtered at less than i-month-sometime.
Beefiness tin can also exist grass-fed or organic.
Diet
The nutritional values below are presented for baked ground veal and broiled patty beef, consisting 85% of lean meat and 15% of fat.
Macronutrients and Calories
Beefiness is overall denser in nutrients, every bit it consists of only 58% h2o, whereas veal contains 67% water.
Calories
Both of these meats are high-calorie foods; even so, beef is significantly higher in calories. I hundred grams of beefiness contains 250 calories, while the same corporeality of veal has 172 calories.
Fats and Cholesterol
Beef contains almost twice the amount of fats found in veal.
The fat content of beef and veal is similar. All the same, veal is slightly higher in polyunsaturated fatty acids, while beef contains more monounsaturated and saturated fats.
Veal is higher in cholesterol.
Protein and Carbohydrates
Beefiness is a little richer in protein; yet, veal contains a significantly higher amount of all essential amino acids. Therefore, the quality of protein from veal is more favorable.
Like most meats, beefiness and veal comprise no notable amount of carbohydrates.
Vitamins
Overall, veal is richer in most vitamins, providing more vitamins B1, B2, B3, B5, and folate or vitamin B9. Veal is also college in vitamin E.
At the same time, beef contains vitamin A, which veal lacks completely. Beef as well provides over twice the corporeality of vitamin B12 compared to veal.
Beef and veal incorporate similar amounts of vitamin B6 and vitamin K.
Both of these meats are absent in vitamin C and vitamin D.
Vitamin Comparison
Vitamin comparison score is based on the number of vitamins past which one or the other food is richer. The "coverage" nautical chart below show how much of the daily needs can be covered by 300 grams of the food
![]()
7
:
2
![]()
Contains more Vitamin Due east +25%
Contains more Vitamin B1 +52.ii%
Contains more Vitamin B2 +53.iv%
Contains more Vitamin B3 +49.3%
Contains more Vitamin B5 +76.three%
Contains more than Folate +22.2%
Contains more Vitamin A +∞%
Contains more Vitamin B12 +107.nine%
Equal in Vitamin B6 - 0.382
Equal in Vitamin Yard - one.2
Contains more Vitamin East +25%
Contains more Vitamin B1 +52.2%
Contains more than Vitamin B2 +53.4%
Contains more Vitamin B3 +49.3%
Contains more Vitamin B5 +76.3%
Contains more Folate +22.ii%
Contains more Vitamin A +∞%
Contains more Vitamin B12 +107.9%
Equal in Vitamin B6 - 0.382
Equal in Vitamin K - 1.two
Minerals
Veal and beef are packed in minerals in dissimilar amounts.
Beef is significantly higher in iron, zinc, and selenium when compared to veal. Beefiness is also a trivial lower in sodium.
Veal, on the other hand, contains larger amounts of magnesium, copper, manganese, phosphorus, and choline.
Veal and beef contain well-nigh the aforementioned levels of calcium and potassium.
Mineral Comparison
Mineral comparison score is based on the number of minerals past which one or the other nutrient is richer. The "coverage" chart below show how much of the daily needs can be covered by 300 grams of the food
![]()
4
:
4
![]()
Contains more than Magnesium +xiv.3%
Contains more Copper +21.2%
Contains more than Iron +162.6%
Contains less Sodium -thirteen.3%
Contains more Zinc +63%
Equal in Calcium - xviii
Equal in Phosphorus - 198
Equal in Potassium - 318
Contains more Magnesium +14.3%
Contains more than Copper +21.2%
Contains more Iron +162.6%
Contains less Sodium -thirteen.iii%
Contains more Zinc +63%
Equal in Calcium - 18
Equal in Phosphorus - 198
Equal in Potassium - 318
Glycemic Index
As beefiness and veal both do not comprise carbohydrates, their glycemic index is considered to exist 0. Y'all tin can read more about the glycemic alphabetize of foods with no carbohydrates here.
Acidity
The acidity of meat is higher immediately later on the slaughter and starts to steadily fall while the meat ages.
The adequate range of the pH value for beefiness falls between 5.3 to v.7, making beefiness acidic (1). Once the pH value of beef reaches 6.5, it starts to decompose.
The pH values for veal are similarly acidic, ranging from five.5 to 6.1, depending on the level of maturity (2).
The potential renal acid load values for veal and beef are 12.1 and 12.6, respectively. The PRAL value demonstrates how much acid or base the given nutrient produces inside the body - the higher this positive number, the more acid-producing the food.
Weight Loss & Diets
Most meats, including beef and veal, are high in calories. Beef contains 78 more calories per every hundred-gram serving compared to veal.
Between these two types of meats, veal is the amend choice for low-calorie and low-fat diets. They both fit well into low carb and low glycemic alphabetize diets.
Various studies have concluded that meat intake, especially processed meats, leads to an increased risk of weight gain and obesity prevalence (three, 4, 5).
Contrastingly, some other study suggested that high-protein, depression-fat diets can be effective in decreasing weight, with both a rich or restricted intake of lean beefiness as red meat (half-dozen).
In weight loss diets, lean, unprocessed meats are brash to exist chosen over fatty and candy meats (7).
Wellness Impact
At present that we have looked at the nutritional differences between beef and veal, we will look at the effects of these two types of meats on wellness.
Health Benefits
Cardiovascular Health
Low in saturated fats, lean beef can have a favorable result on cardiovascular disease lipid take a chance factors, decreasing total cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein levels (8). Veal is likewise lower in saturated fat acids, being lower in fats.
One study has shown that a salubrious nutrition high in protein, with or without reddish meat, may improve cardiometabolic disease adventure factors (seven).
Diabetes
A diet low in calories and high in protein from lean cherry-red meats has been studied to amend run a risk markers of blazon 2 diabetes mellitus (9).
Downsides and Risks
Cardiovascular Health
Despite the previous findings, research has shown that consumption of unprocessed just especially processed red meat leads to a small-scale increased risk of cardiovascular disease and all-crusade bloodshed (10). Commutation of poly peptide from soy, nuts, and legumes instead of red meat has been associated with a lower risk of cardiovascular illness (xi).
These adverse effects are said to be caused by a chemical establish in the blood subsequently eating red meat, called trimethylamine N-oxide or TMAO (12)
Diabetes
Similarly, unprocessed and specially candy red meat has been correlated with a higher risk of diabetes. This take a chance may be partly due to the contents of heme iron and dietary cholesterol found in red meat (xiii). Every bit veal is lower in both heme iron and dietary cholesterol, information technology can be assumed that veal is the better pick between these two kinds of meat for people with prediabetes or diabetic weather condition.
Cancer
Consumption of red meats, in item candy cherry meat, has long been associated with an increased risk of several types of cancer.
Total cherry meat intake increases the risk of colorectal, nasopharynx, lung, pancreas, breast, and prostate cancer (14, xv, 16).
In addition, processed red meat too elevates the adventure of squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus and non-cardia stomach cancer (14).
References
- The effect of pH on beef eating quality
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/283006713
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/manufactures/PMC2697260/
- https://bmcnutr.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s40795-016-0063-9
- https://www.researchgate.internet/publication/5501979
- https://world wide web.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/manufactures/PMC5598025/
- https://academic.oup.com/ajcn/article/108/1/33/5036105
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3238465/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31771921/
- https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamainternalmedicine/fullarticle/2759737
- https://www.bmj.com/content/371/bmj.m4141
- Eating ruddy meat daily triples middle disease-related chemical
- https://world wide web.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3483430/
- https://world wide web.wcrf.org/dietandcancer/exposures/meat-fish-dairy
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31389007/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6171413/
Infographic
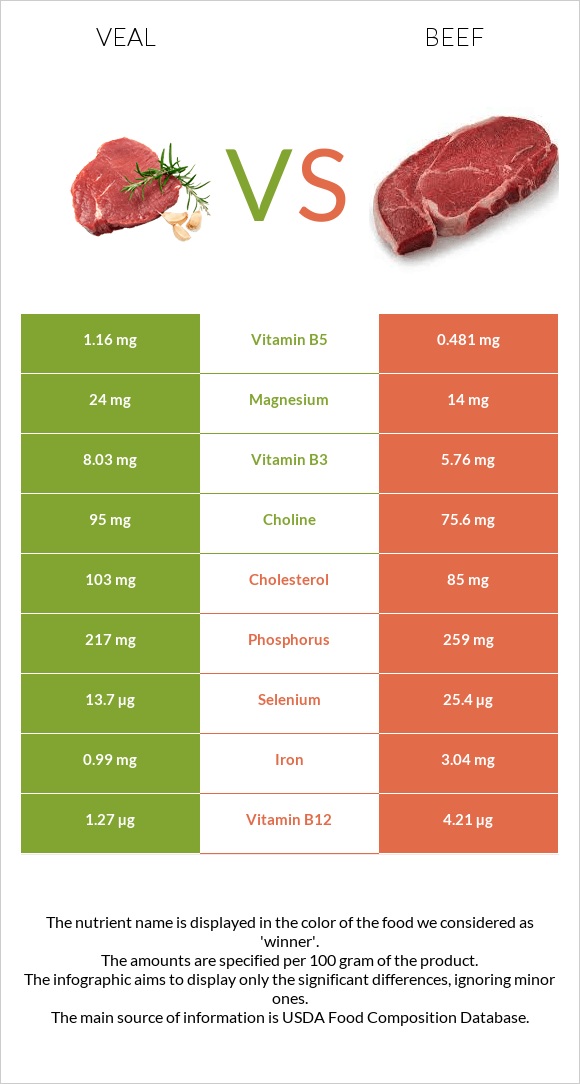
Which food is preferable for your diet?
![]()
![]()
is ameliorate in case of low nutrition
 |  | |
| Low Fats nutrition | | |
| Low Carbs diet | Equal | |
| Low Calories diet | | |
| Depression glycemic index diet | Equal | |
People also compare
Vitamin and Mineral Summary Scores
The summary score is calculated by summing up the daily values contained in 300 grams of the production. Obviously the more the food fulfills man daily needs, the more the summary score is.
Vitamin Summary Score
47
![]()
52
![]()
Mineral Summary Score
42
![]()
55
![]()
Macronutrients Comparison
Macronutrient comparison charts compare the amount of protein, total fats, and full carbohydrates in 300 grams of the food. The displayed values evidence how much of the daily needs can be covered past 300 grams of food.
Protein
146%
![]()
156%
![]()
Carbohydrates
0%
![]()
0%
![]()
Fats
35%
![]()
71%
![]()
Comparison summary
Which food is lower in Saturated Fat?
![]()
Veal is lower in Saturated Fat (difference - ii.855g)
Which nutrient is richer in vitamins?
![]()
Veal is relatively richer in vitamins
Which food contains less Sodium?
![]()
Beefiness contains less Sodium (deviation - 11mg)
Which food is lower in Cholesterol?
![]()
Beef is lower in Cholesterol (divergence - 15mg)
Which nutrient is cheaper?
![]()
Beef is cheaper (difference - $0.2)
Which food contains less Sugar?
?
The foods are relatively equal in Saccharide (0 chiliad)
Which food is lower in glycemic alphabetize?
?
The foods have equal glycemic indexes (0)
Which nutrient is richer in minerals?
?
Information technology cannot be stated which food is richer in vitamins. See the charts below for detailed information. See the charts below for detailed information. See the charts beneath for detailed data.
Source: https://foodstruct.com/compare/veal-vs-beef#:~:text=bound%20with%20it.-,Appearance,is%20also%20higher%20in%20iron.

0 Response to "Does Veal Have More Iron Than Beef"
Post a Comment